07 Are There Traces of Hepatophilic Virus in Your Body
– Appearance of the Skin
The appearance of the skin of a chronic hepatitis patient is rather complicated. This is because when chronic hepatitis virus causes dysfunction of the liver, it will lead to abnormality of metabolism. That will show on the skin. So the appearance of the skin furnishes a certain degree of value for clinical reference in diagnosing chronic hepatitis as follows:
1) Acne
Acne is caused by the sebaceous gland stimulated by testosterone in the human body. Chronic virus hepatitis often brings down immunologic function and causes endocrine dyscrasia, disorder of absorption of microelements and a disturbance of metabolism. That is the main cause for acne trouble among young people. Systematic medication with traditional Chinese medicine can cure active chronic virus hepatitis and acne is cured automatically, but extensive scars may remain on the face, chest and back.
2) Itching
A chronic hepatitis patient may suffer from itching on the skin no matter it is a case of jaundice or not. This is particularly so in the early stage of active chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Clinical diagnosis often shows the activity of rising dampness and heat, accompanied with itching, and light red spots and desquamation (mostly between the brows, besides the wings of the nose, on the earlobes or behind ears), and in some serious cases damages to the skin (particularly during climacterium). It is generally believed that itching is the result of stimulation of the nerve endings by cholate caused by hepatitis. On a chronic hepatitis patient are often found pachylosis, desquamation, thickening, lichenification and pigmentation of the skin. A case of limited symptoms would often be mistaken for neurodermatitis or eczema.
3) Dermatoxerasia Complex
Affection of hepatophilic virus in infancy resulting in virus hepatitis may lead to skin diseases because of the virus as antigen, including eczema, urticaria, neuroedema, lichen (papular urticaria). Eczema is common in such cases among infants and children, displaying in the form of effusion, xeroderma or the seborrheic type. An eczema case may be light or serious on and off, capable of recurrence and lasting into adulthood. It often manifests as xeroderma complex among young children, forming pigmentation, desquamation, rhagas, and itching. The affected areas are mostly on the lower limbs and the abdomen. The ailment will subside when the patient reaches adulthood, but dot or patch pigmentation will remain, and in some cases, with xeroderma complex which will result in coarse skin, rhagas and pigmentation, mostly on the lower limbs, chest and back.
4) Pigmentation
Pigmentation seems to be closely linked with the length and gravity of a hepatitis case. It is generally believed that it is caused by increase of estrogen and hypoadrenalism. The exposed parts of the skin of a hepatitis patient (such as the face and around eyes) will show darkness, accompanied by pigmentation, at an incidence of 20%. When a case of chronic hepatitis has developed to the stage of deficiency of vital essence in the liver and kidneys, the skin of the patient will turn dark all over, often accompanied with dots or patches of pigmentation in the face, limbs, abdomen and back. Such spots and patches of pigmentation may be mistaken for senile plaques. After systematic medication with Chinese medicine, the patches will turn light, shrink or even disappear. In the case cirrhosis, there tends to show concentrated patches of pigmentation or telangiectasis on the lower limbs.
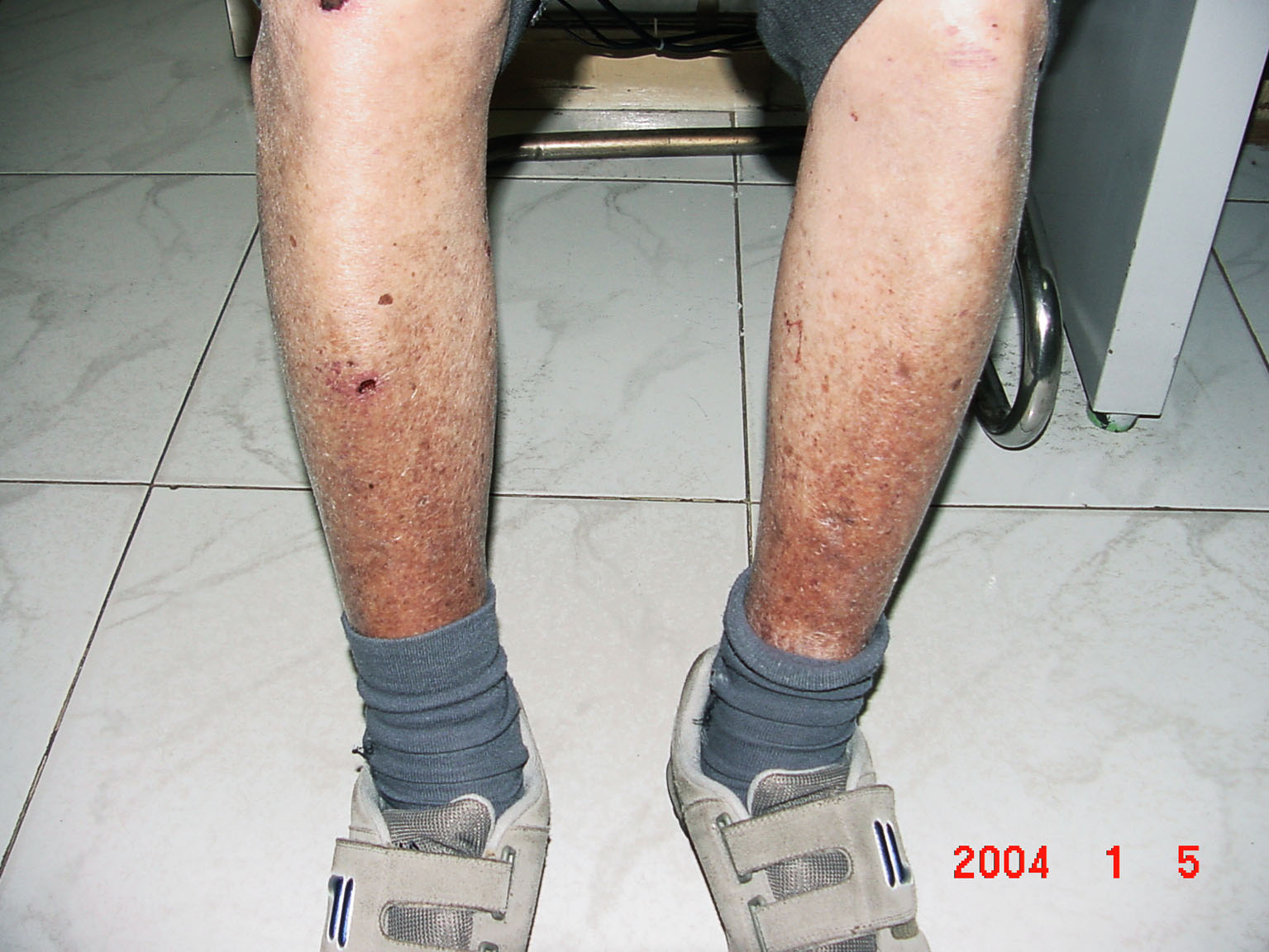
5) Subcutaneous hemorrhage and Purpura
A patient affected by chronic hepatophilic virus often has the tendency of hemorrhage or actual hemorrhage. This is because of the deterioration of synthesis of coagulation factors, over spending of them, deficiency of the material for making coagulation factors, hypersplenism, the increase of the fragility of the blood capillaries. It is partially shown in the forms of eccymosis, bleeding of the nose and gum, or hematemesis, hematochezia, or/and urohematin. A normal liver is capable of producing all of hemopexin needed and a hepatitis patient usually suffers from coagulation disorder. Statistics show that 85% of hepatitis patients show disorder in coagulation tests, 15% of them suffer from hemorrhage. Bleeding mainly from the skin and membrane and in serious cases in the digestive system and urinary tracts. When hemorrhage becomes grave, the loss of blood may lead to anemia, shock or even death. So it is not uncommon to find patients of late stage hepatitis die from hemorrhage as a result of coagulation disorder.
6) Xanthoma
In the case of chronic hepatic insufficiency, the level of serum fat and cholesterol will remain high continuously, causing the accumulation of fat which, after being devoured by histiocytes, will grow into xanthoma. Flat xanthomas often appear on eyelids, palms, the neck, chest or back and nodular xanthomas appear on wrists, elbows, knees and ankles and buttocks. 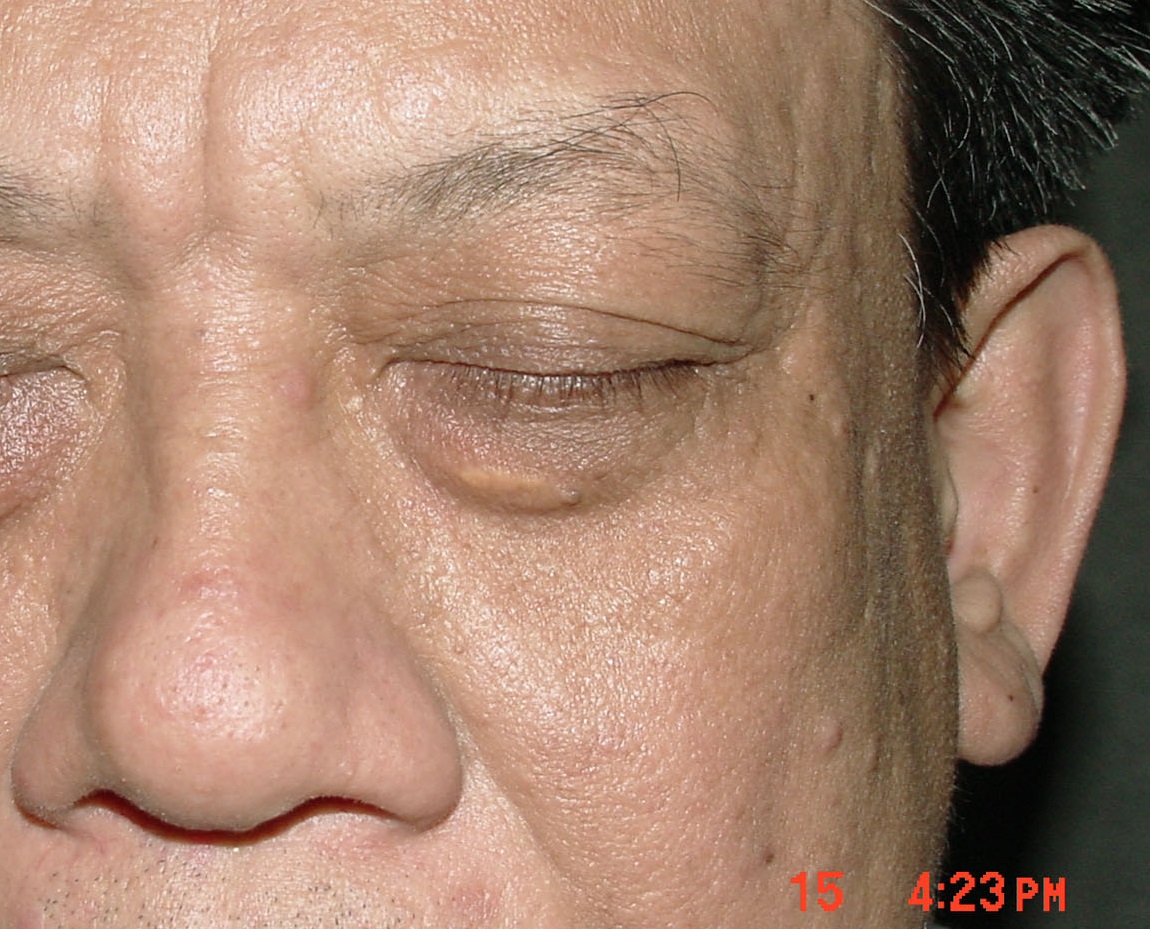
7) White Nails
Hepatitis patients often show white nails, with a red line between the further end and the base of a nail. That is an indication of the lower level of serum albumin.
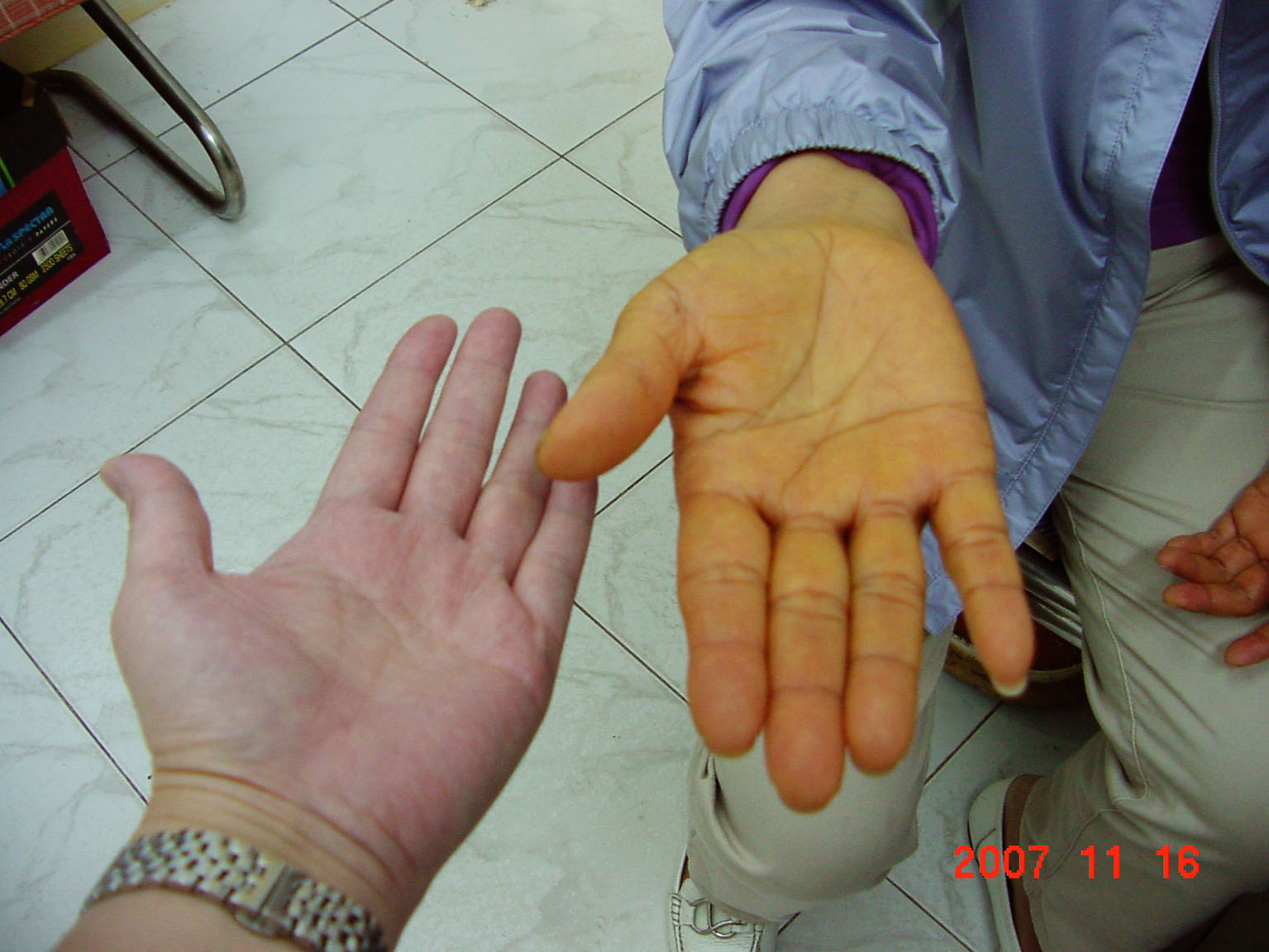
8) Liver Palms, Spider Moles, Face Erythema and Telangiectasis
Those symptoms cited above may appear on hepatitis and cirrhosis victims. They have something to do with the increase of estrogen, greater capillary permeability caused by immune complex angiitis, vena portae or venous hypertension in the lower part of the trunk, thromb.
 (Photo showing lupus erythematosus on the skin around eyelids.)
(Photo showing a decrease of erythema after treatment of lupus erythematosus with medication of traditional Chinese medicine)
(Photo showing lupus erythematosus on the skin around eyelids.)
(Photo showing a decrease of erythema after treatment of lupus erythematosus with medication of traditional Chinese medicine)
9) Extensive Heat Rash and Tinea Corporis
Owing to a deterioration of immunologic function resulting from affection of hepatophilic virus, ailments caused by infection of bacteria or candidae are common, especially heat rash, tinea corporis, tinea on limbs and pyodermia, candida paronychia, and vaginitis. When the virus hepatitis is cured clinically, it will be easy to control bacteria or fungus infection of the skin and cure them clinically.
(Photo showing subcutaneous venous aneurysm and heat rash on the abdomen and lower chest)
(Photo showing extensive heat rashes on the abdomen)
Although many of the skin ailments belong to the department of dermatology and they show different appearances, attention should be paid to abnormal immunity reaction after a liver disease if the liver dullness appears abnormal. When the systematic medication with traditional Chinese medicine has cured hepatitis, many cases of skin infection show marked improvement or are cured completely.

(Photo showing lupus erythematosus on the skin around eyelids.) (Photo showing a decrease of erythema after treatment of lupus erythematosus with medication of traditional Chinese medicine)

